Borderline Lepromatous Leprosy with Mild Reversal Reaction in Child
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Childhood leprosy is an important marker of the status of the ongoing leprosy control program, as it is an indicator of active disease transmission in the community. Children are believed to be the most vulnerable group to infection with M. leprae due to their immature or nascent immunity and exposure to intrafamilial contacts.
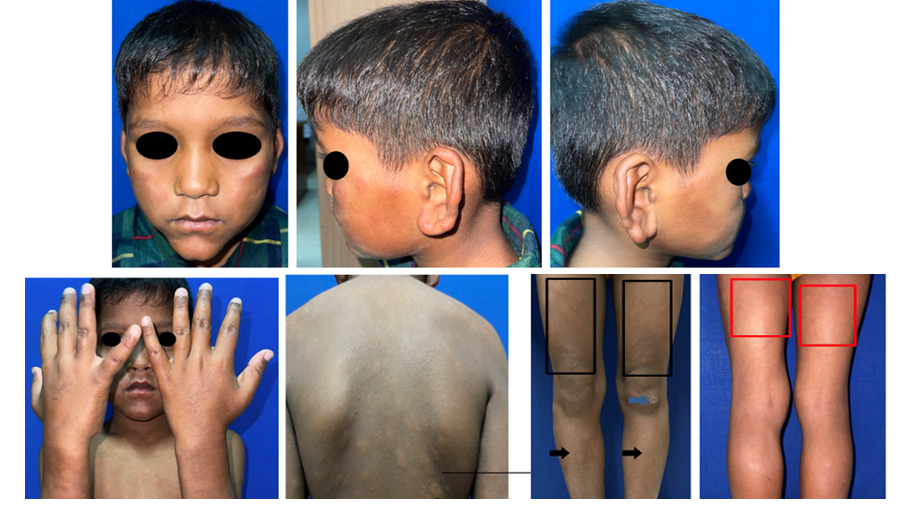
Case report: A 8 years ole male patient presented with hypopigmented patch and erythematous patch with not itchy, not pain, and loss of sensation which increasing more since 1 week ago. Initially 2 months ago, white patch that felt numbness appeared on the back, then white patches wider and spread to the chest, both arms and thighs. Dermatologic finding showed erythematous plaques, hypopigmentation macule with infiltration on cheek, back, both of arms, xerosis cutis. Decreased sensory function was found in the median, ulnar and posteriol tibial nerves. Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) staining revealed bacterial index (BI) +5 and morphological index (MI) 80%. Histopathological examination showed atrophic stratified squamous epithelium, grenz zone, many groups of foamy macrophages reached the fat layer. The patient was diagnosed Morbus Hansen borderline lepromatous leprosy type with mild reversal reaction and treated with MDT-MB drug package, vitamin B complex tablet, zinc tablet, paracetamol tablet, and 10% urea cream on dry skin 2 times a day on dry skin after bath during 2 month and the lesion was reduced.
Conclusion: The rate of childhood leprosy continues to be a significant problem. There is a clear need to strengthen early detection, treatment, and regular follow up of these cases in both high and low endemic setting is essential in the prevention of deformities.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
Global Leprosy Strategy 2016-2020: Accelerating towards a Leprosy Free World, WHOs SEARO/Department of control of Neglected Tropical Diseases. New Delhi; 2016.
World Health Organization. Global leprosy (Hansen disease) update, 2019: time to step-up prevention initiaves. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2020;95:417–40.
Gunawan H, Kamilia A, Menaldi SL, Marissa M, Prakoeswa CR AM. Characteristics of Grade 2 Disability in Indonesia Children with Leprosy : A Five-Year Multicenter Retrospective Study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:1–5.
Sakral A, Dogra N, Dogra D, Sharma K. Clinical and epidemiological trends in childhood leprosy: A 20-year retrospective analysis from a tertiary care hospital in Jammu, North India. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2022;88(6):755-760.
Bhat RM PC. Leprosy: an overview of pathophysiology. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2012;2012:181089.
World Health Organization. Toward zero leprosy, Global Leprosy (Hansen’s disease) Strategy 2021-2030. Geneva: WHO; 2021.
Penna MLF, Penna GO, Iglesias PC, Natal S RL. Anti-PGL-1 Positivity as a Risk Marker for the Development of Leprosy among Contacts of Leprosy Cases: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop DiS. 2016;10(5):e0004703.
Desikan KV, Rao KV, Bharambe MS RP. Appraisal of skin smear reports of field laboratories. Lepr Rev. 2006;77(4):311–6.
Scollard DM, Adams LB, Gillis TP et al. The continuing challenges of leprosy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:338–81.
Barreto JG, Frade MA, Filho FB, Silva M, Spencer JS SC. Leprosy in Children. Curr Innfect Rep. 2017;19:23.
Perhimpunan Dokter Spesialis Kulit dan Kelamin Indonesia (PERDOSKI). Panduan Praktik Klinis bagi Dokter Spesialis Kulit dan Kelamin di Indonesia. Jakarta: PERDOSKI; 2017.
Coll HS, Mora HR, Beltran JC, Duthie MS CN. Social and environmental conditions related to Mycobacterium leprae infection children and adolescents from three leprosy endemic regions of Colombia. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19:520.