Role of Intraoperative Frozen Section in Determining the Margin of Excision in Case of Eyelid Nodular Hidradenoma
Main Article Content
Abstract
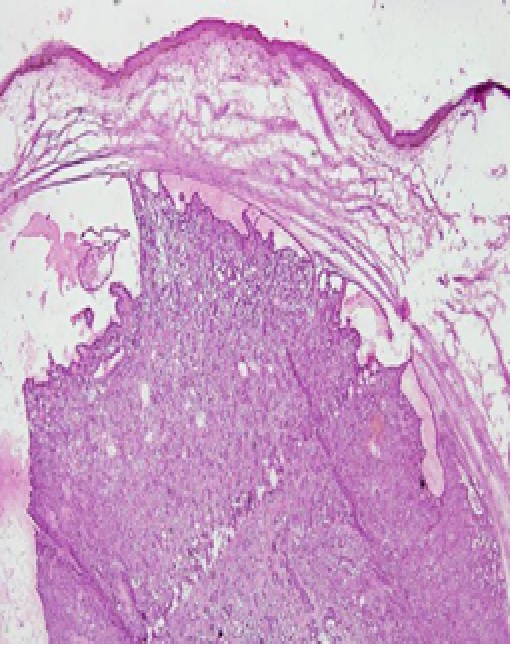
Background: Nodular hidradenoma is a rare benign skin adnexal tumor originating from sweat glands. It can recurrence and possibly future malignant transformation. An intraoperative frozen section guides the operation and provides margin control.
Case report: We reported a case of a 54 year old woman with a lump under the right eyelid who was early diagnosed with suspected basalioma. The lump was initially small as the size of a green bean seed, but grew in these five months to the size of a corn kernel, itchy and sometimes bleeds. A dermoscopic examination showed a nodule with yellowish globules and arborizing vessels. An intraoperative frozen section procedure was performed with a diagnosis of benign lesion and tumor-free incision margins. The patient's final diagnosis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue was nodular hidradenoma.
Conclusion: Frozen section intraoperative is very useful to prevent recurrence and malignant transformation of nodular hidradenoma. Eyelid tumors, in particular, have shown benefit from frozen section margin assessment for cosmetic or functional purposes.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.